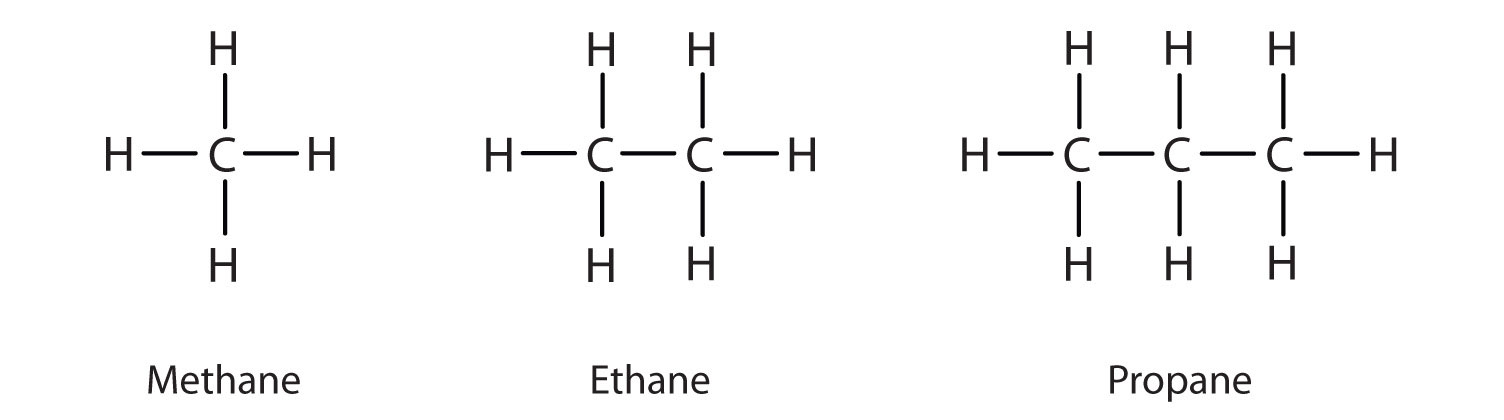
The term ‘hydrocarbon’ is self-explanatory which means compounds of carbon and hydrogen only.
- LPG is the abbreviated form of liquified petroleum gas whereas CNG stands for compressed natural gas.
- Another term ‘LNG’ (liquified natural gas) is also a fuel and is obtained by liquifaction of natural gas.
- Petrol, diesel and kerosene oil are obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum found under the earth’s crust.
- Coal gas is obtained by the destructive distillation of coal.
- Natural gas is found in upper strata during drilling of oil wells. The gas after compression is known as compressed natural gas.
- LPG is used as a domestic fuel with the least pollution.
- All these fuels contain mixture of hydrocarbons, which are sources of energy.
- Hydrocarbons are also used for the manufacture of polymers like polythene, polypropene, polystyrene etc.
- Higher hydrocarbons are used as solvents for paints.
CLASSIFICATION OF HYDROCARBONS:-
Depending upon the types of carbon-carbon bonds, they can be classified into three main categories –
- Saturated
- Unsaturated and
- Aromatic hydrocarbons.
Saturated hydrocarbons contain carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds.
If different carbon atoms are joined together to form open chain of carbon atoms with single bonds, they are termed as alkanes.
On the other hand, if carbon atoms form a closed chain or a ring, they are termed as cycloalkanes.
Cycloalkanes again only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds, but this time the carbon atoms are joined up in a ring. The smallest cycloalkane is cyclopropane.

Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds –double bonds, triple bonds or both.
Aromatic hydrocarbons are a special type of cyclic compounds.
You can construct a large number of models of such molecules of both types (open chain and close chain) keeping in mind that carbon is tetravalent and hydrogen is monovalent.
For making models of alkanes, you can use toothpicks for bonds and plasticine balls for atoms. For alkenes, alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons, spring models can be constructed.