Role of Indian Railways
Since its inception, Indian Railways has successfully played the role of the prime carrier of goods and passengers in the Indian subcontinent. As the principal
Share Your Information
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Since its inception, Indian Railways has successfully played the role of the prime carrier of goods and passengers in the Indian subcontinent. As the principal

(1) 1959(2) 1965(3) 1976(4) 1982 Ans. (3) (l) heat is absorbed(2) heat is released(3) heat remains unchanged(4) None of these Ans. (2) (1) Xenon(2) Argon(3)
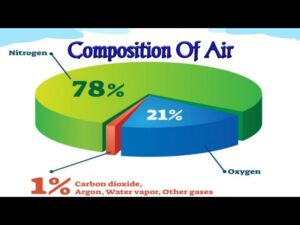
Atmospheric air contains many gaseous components as well as water vapor and miscellaneous contaminants (e.g., smoke, pollen, and gaseous pollutants not normally present in free


● India’s very first Solar Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Station was inaugurated at the Karnal Lake Resort.● Inauguration of this Charging Station was done by

Indian comic book cartoon character, Chacha Chaudhary has been declared as the official mascot for the centrally-sponsored Namammi Gange Programme on October 1, 2021. The

● PM Narendra Modi on November 5, 2021 inaugurated the reconstructed Shri Adi Shankaracharya Samadhi (final resting place) at the premises of the Kedarnath Temple

Economic development implies the process of securing levels of productivity in all sectors of the economy and this, in turn, is a function of the

Development is a process and the process is multi-dimensional. The major indicators to measure the levels of development are: Net National Product (NNP):• Net national
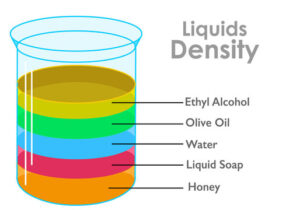
The density ρ of a fluid is its mass per unit volume. The densities of air and water at standard conditions of 20°C and 101.325
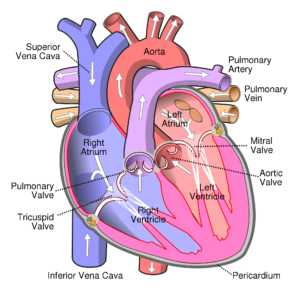
The heart is a fist-sized organ that pumps blood throughout your body. It’s the primary organ of our circulatory system. Our heart contains four main

The human body is a biological machine made of body systems; groups of organs that work together to produce and sustain life. Sometimes we get lost while

What is Momentum It is the quantity of motion of a moving body & may be defined as a product of mass and velocity. Its

Law of conservation of momentum states Ans: (d) Law of conservation of momentum can be defined in any of these three ways. Law of conservation
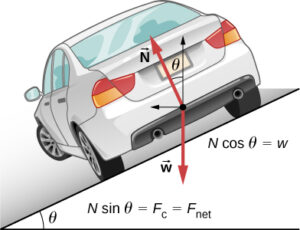
) When a motorcar makes a sharp turn at a high speed, we tend to get thrown to one side because we tend to continue in our straight line motion and an unbalanced force is applied by the engine of the motorcar changes the direction of motion of the motorcar. So, we slip to one side of the seat due to the inertia of our body.

Force and Laws of Motion (MCQ) By applying a force of one Newton, one can hold a body of mass (a) 102 grams (b) 102

Balancing a chemical equation involves a certain amount of trial and error. In general, however, you should follow these steps:
Count each type of atom in reactants and products. Does the same number of each atom appear on both sides of the arrow? If not, the equation is not balanced, and you need to go to step…..

Acids and bases react with one another to yield two products: water, and an ionic compound known as a salt. This kind of reaction is called a neutralization reaction. All alkalis are bases, but all bases are not alkalis……
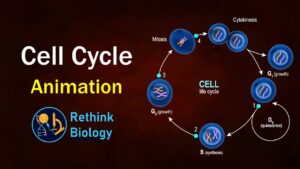
This is the most dramatic period of the cell cycle, involving a major reorganisation of virtually all components of the cell. Since the number of
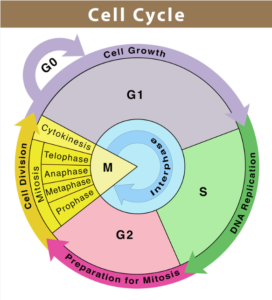
The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesizes the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells
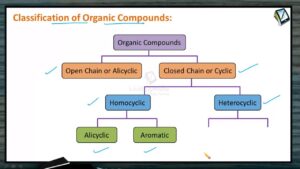
Organic compounds are broadly classified as follows:
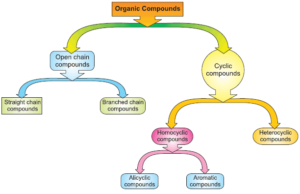
SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES The element carbon has the unique property called catenation due to which it forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.
Predict, qualitatively, how an external force will affect the speed and direction of an object’s motion. Explain the effects with the help of a free body diagram. Use free body diagrams to draw position, velocity, acceleration and force graphs and vice versa.
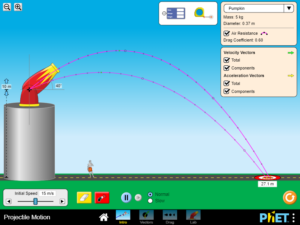
Determine how each parameter (initial height, initial angle, initial speed, mass, diameter, and altitude) affects the trajectory of an object, with and without air resistance. Predict how varying the initial conditions will affect a projectile’s path, and provide an explanation for the prediction.
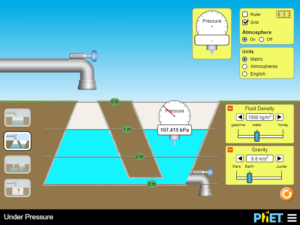
Describe how pressure changes in air and water as a function of depth. Describe what variables affect pressure. Predict pressure in a variety of situations.
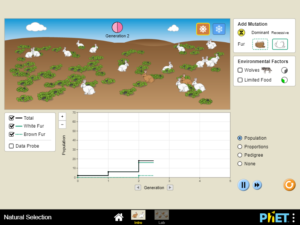
Determine which mutations are favored by the selection agents of predators and food variety and which mutations are neutral. Describe which traits change the survivability of an organism in different environments. Track genes through multiple generations.
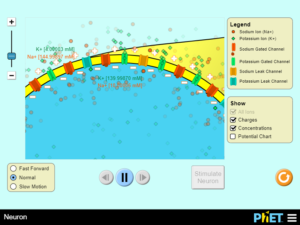
Describe why ions can or cannot move across neuron membranes. Identify leakage and gated channels, and describe the function of each. Describe how membrane permeability changes in terms of different types of channels in a neuron

Explain the main sequence of events that occur within a cell that leads to protein synthesis. Predict how changing the concentrations and interactions of biomolecules affects protein production. Explain how protein production in a single cell relates to the quantity produced by a collection of cells.
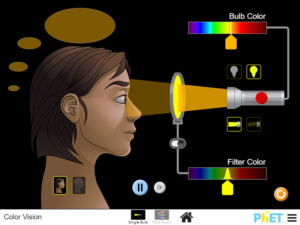
Determine what color the person sees for various combinations of red, green, and blue light. Describe the color of light that is able to pass through different colored filters.
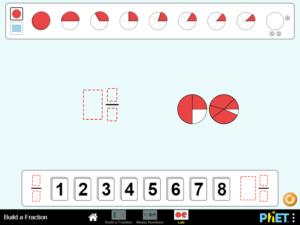
Build equivalent fractions using numbers and pictures. Compare fractions using numbers and patterns. Recognize equivalent simplified and un-simplified fractions
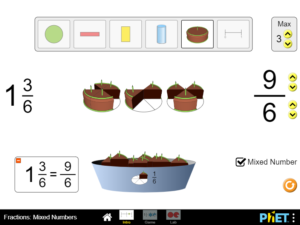
Predict and explain how changing the numerator of a fraction affects the fraction’s value. Predict and explain how changing the denominator of a fraction affects the fraction’s value.
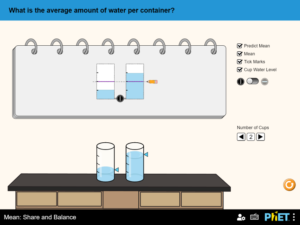
Justify how the mean is calculated. Describe the mean in terms of leveling, fair share, and balance point. Predict the effects of (an) outlier(s) on the mean.
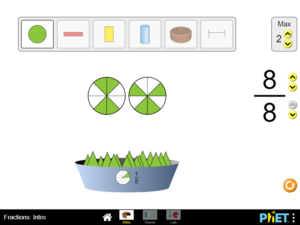
Predict and explain how changing the numerator of a fraction affects the fraction’s value. Predict and explain how changing the denominator of a fraction affects the fraction’s value…..
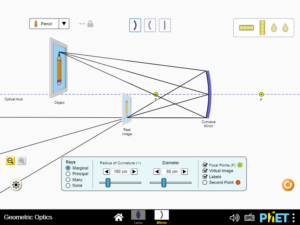
Explain how an image is formed by a converging or diverging lens or mirror using ray diagrams. Determine how changing the parameters of the optic (radius of curvature, index of refraction) affects where the image is formed and how it appears (magnification, brightness, and inversion).
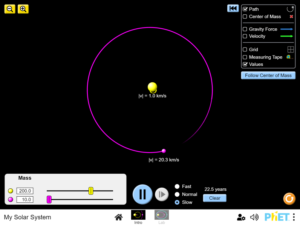
Predict how the position, mass, velocity, and distance between planetary bodies affect their motion and orbits. Illustrate how the gravitational force controls the motions of the planets…..

The alkali metal halides, MX, (X=F,Cl,Br,I) are all high melting, colourless crystalline solids. They can be prepared by the reaction of the appropriate oxide, hydroxide

Benzene was considered as parent ‘aromatic’ compound. Now, the name is applied to all the ring systems whether or not having benzene ring, possessing following
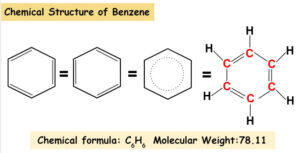
Benzene and polynuclear hydrocarbons containing more than two benzene rings fused together are toxic and said to possess cancer producing (carcinogenic) property. Such polynuclear hydrocarbons
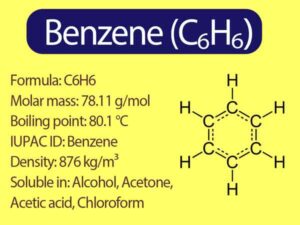
Ethyne on passing through red hot iron tube at 873K undergoes cyclic polymerization. Three molecules polymerise to form benzene, which is the starting molecule for

Preparation of Alkanes Typography is the art and technique Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable and

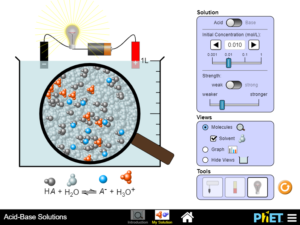
Describe how common tools (pH meter, conductivity, pH paper) help identify whether a solution is an acid or base and strong or weak and concentrated or dilute…..
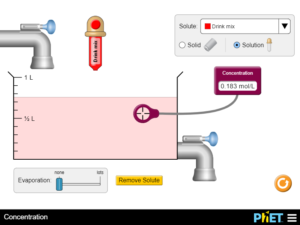
Describe the relationships between volume and amount of solute to solution concentration. Explain how solution color and concentration are related. Predict how solution concentration will change for any action (or combination of actions) that adds or removes water, solute, or solution, and explain why……
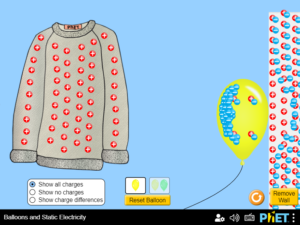
Describe and draw models for common static electricity concepts (transfer of charge, induction, attraction, repulsion, and grounding). Make predictions about force at a distance for various configurations of charge. ……

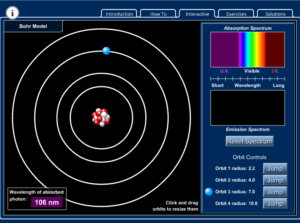
Explore how light interacts with molecules in our atmosphere. Identify that absorption of light depends on the molecule and the type of light……
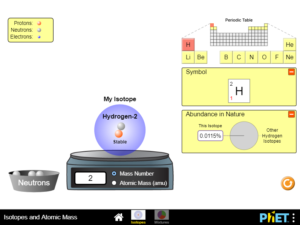
Define “isotope” using mass number, atomic number, number of protons, neutrons and electrons. Given information about an element, find the mass and name of an isotope.
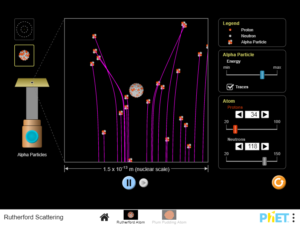
Describe the qualitative difference between scattering off positively charged nucleus and electrically neutral plum pudding atom. For charged nucleus, describe qualitatively how angle of deflection depends on: Energy of incoming particle, Impact parameter, Charge of target……
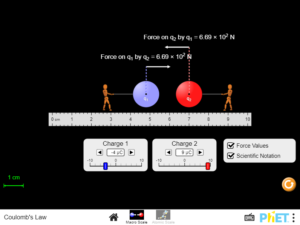
Relate the electrostatic force magnitude to the charges and the distance between them. Explain Newton’s third law for electrostatic forces…….
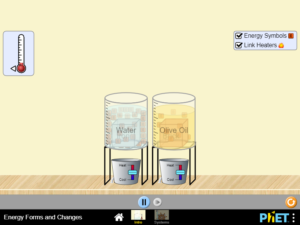
Predict how energy will flow when objects are heated or cooled, or for objects in contact that have different temperatures. Describe the different types of energy and give examples from everyday life. Describe how energy can change from one form of energy into another. ……
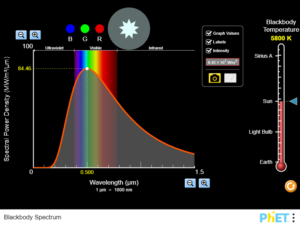
Describe what happens to the blackbody spectrum as you increase or decrease the temperature. What happens to the shape of the curve and the peak of this curve? Describe the blackbody spectrum of a light bulb. Why do light bulbs get hot? Do they seem efficient? ……..
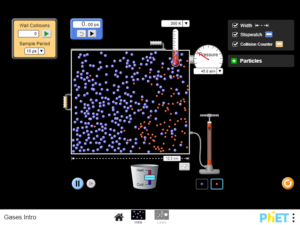
Describe the behavior of the gas particles in the box. Identify the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and number of gas molecules..,
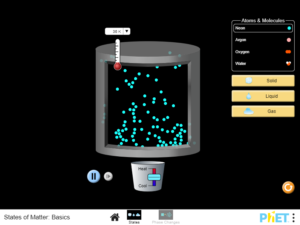
Describe characteristics of three states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Predict how varying the temperature or pressure changes the behavior of particles….
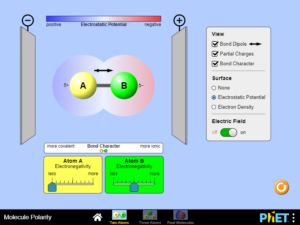
Predict bond polarity using electronegativity values. Indicate polarity with a polar arrow or partial charges…..
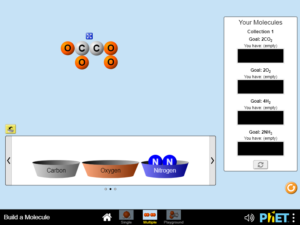
Describe the difference between an atom and a molecule. Build simple molecules from atoms. Distinguish between the coefficient and subscript in a chemical formula…..
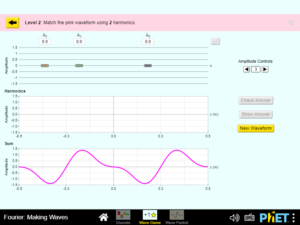
Explain qualitatively how sines and cosines add up to produce arbitrary periodic functions. Recognize that each Fourier component corresponds to a sinusoidal wave with a different wavelength or period. Describe sounds in terms of sinusoidal waves……
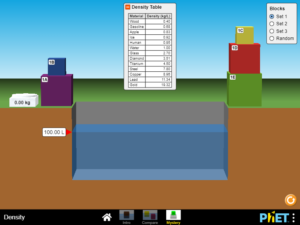
Describe how the concept of density relates to an object’s mass and volume. Explain how objects of similar mass can have differing volume, and how objects of similar volume can have differing mass….
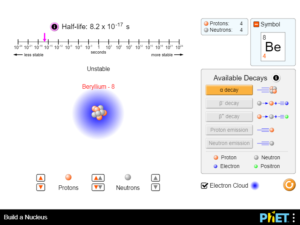
Explain how the changing the number of neutrons or protons affects the atomic number and isotope species. Describe how different decays will change the nucleons in the nucleus and if that changes the symbol of the atom being shown and affects parameters like atomic number/atomic mass…..

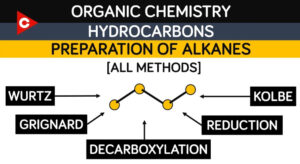
Petroleum and natural gas are the main sources of alkanes. However, alkanes can be prepared by following methods : Dihydrogen gas adds to alkenes and


