Force and Laws of Motion (MCQ)
By applying a force of one Newton, one can hold a body of mass (a) 102 grams (b) 102 kg (c) 102 mg (d) None of these
Ans: (a) By applying a force of one Newton, one can hold a body of mass 102 grams.
Friction forces act (a) in the direction of force applied (b) in the direction of the motion (c) in the direction opposite to the direction of motion (d) None of these
Ans: (b) Friction forces act in the direction opposite to the direction of motion.
The effect of frictional force may be minimized by (a) using a smooth object (b) using a smooth plane (c) providing a lubricant at the surface of contact (d) All of these
Ans: (d) The effect of frictional force may be minimized by using a smooth object, using a smooth plane or by providing a lubricant at the surface of contact.
When a bus suddenly starts, the standing passengers lean backwards in the bus. It is an example of (a) Newton’s first law (b) Newton’s second law (c) Newton’s third law (d) None of Newton’s law
Ans: (a) When a bus suddenly starts, the standing passengers lean backwards in the bus. It is an example of Newton’s first law
Momentum has the same units as that of (a) couple (b) torque (c) impulse (d) force
Ans: (c) Momentum has the same units as that of impulse
When a force of newton acts on a mass of 1 kg that is free to move, the object moves with a (a) speed of 1 m/s (b) speed of 1 km/s (c) acceleration of 10 m/s2 (d) acceleration of 1m/s2
Ans: (d) When a force of newton acts on a mass of 1 kg that is free to move, the object moves with a acceleration of 1m/s2
If an object experience a net zero unbalanced force, then the body (a) can be accelerated (b) moves with constant velocity (c) cannot remain at rest (d) None of these
Ans: (b) If an object experience a net zero unbalanced force, then the body moves with constant velocity
A hockey player pushes the ball on the ground. It comes to rest after travelling certain distance because (a) the player stops pushing the ball (b) no unbalanced force action on the wall (c) the ball moves only when pushes (d) the opposing force acts on the body.
Ans: (d) A hockey player pushes the ball on the ground. It comes to rest after travelling certain distance because the opposing force acts on the body.
The physical quantity which is the product of mass and velocity of a body is known as (a) inertia (b) momentum (c) force (d) change in momentum
Ans: (b) The physical quantity which is the product of mass and velocity of a body is known as momentum
Rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the (a) balanced force applied (b) applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force (c) time during which the force is applied (d) All of these
Ans: (b) Rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force.
A book of weight 10 N is placed on a table. The force exerted by the surface of the table on the book will be (a) Zero (b) 10 N (c) 20 N (d) None of these
Ans: (b) A book of weight 10 N is placed on a table. The force exerted by the surface of the table on the book will be 10 N
When a body is stationary- (a) There is no force acting on it (b) The force acting on it not in contact with it (c) The combination of forces acting on it balances each other (d) The body is in vacuum
Ans: (c) When a body is stationary- The combination of forces acting on it balances each other
A rider on horse falls back when horse starts running, all of a sudden because (a) rider is taken back (b) rider is suddenly afraid of falling (c) inertia of rest keeps the upper part of body at rest while lower part of the body moves forward with the horse (d) None of the above
Ans: (c) A rider on horse falls back when horse starts running, all of a sudden because inertia of rest keeps the upper part of body at rest while lower part of the body moves forward with the horse
A man getting down a running bus, falls forward because (a) due to inertia of rest, road is left behind and man reaches forward (b) due to inertia of motion upper part of body continues to be in motion in forward direction while feet come to rest as soon as they touch the road (c) he leans forward as a matter of habit (d) of the combined effect of all the three factors stated in (a), (b) and (c)
Ans: (b) A man getting down a running bus, falls forward because due to inertia of motion upper part of body continues to be in motion in forward direction while feet come to rest as soon as they touch the road
A force 10 N acts on a body of mass 20 kg for 10 sec. Change in its momentum is (a) 5 kg m/s (b) 100 kg m/s (c) 200 kg m/s (d) 1000 kg m/s
Ans: (b) A force 10 N acts on a body of mass 20 kg for 10 sec. Change in its momentum is 100 kg m/s
Swimming is possible on account of (a) first law of motion (b) second law of motion (c) third law of motion (d) newton's law of gravitation
Ans: (c) Swimming is possible on account of third law of motion
A man is at rest in the middle of a pond on perfectly smooth ice. He can get himself to the shore by making use of Newton's (a) first law (b) second law (c) third law (d) all the laws
Ans: (c) A man is at rest in the middle of a pond on perfectly smooth ice. He can get himself to the shore by making use of Newton's third law
A cannon after firing recoils due to- (a) conservation of energy (b) backward thrust of gases produced (c) Newton's third law of motion (d) Newton's first law of motion
Ans: (c) A cannon after firing recoils due to- Newton's third law of motion
Newton's third law of motion leads to the law of conservation of- (a) angular momentum (b) energy (c) mass (d) momentum
Ans: (d) Newton's third law of motion leads to the law of conservation of- momentum
Rockets work on the principle of conservation of (a) energy (b) mass (c) momentum (d) All of these
Ans: (c) Rockets are examples of third law of motion, i.e. the law of conservation of momentum.
The force of friction acting on a car on different roads in the increasing order of magnitude will be (a) mud, tar, concrete and gravel roads (b) tar, concrete, gravel and mud roads (c) concrete, tar, gravel and mud roads (d) gravel, mud, tar and concrete roads
Ans: (c) The force of friction acting on a car on different roads in the increasing order of magnitude will be concrete, tar, gravel and mud roads
Inertia is that property of a body by virtue of which the body is (a) unable to change by itself the state of rest (b) unable to change by itself the state of uniform motion (c) unable to change by itself the direction of motion (d) All of the above
Ans: (d) Newton’ first law of motion is also called law of inertia as it defines inertia.
An object will continue moving uniformly when (a) the resultant force on it is increasing continuously (b) the resultant force is at right angles to its rotation (c) the resultant force on it is zero (d) the resultant force on it begins to decrease
Ans: (c) The body will continue accelerating until the resultant force acting on the body becomes zero.
We can derive Newton’s (a) second and third laws from the first law (b) first and second laws from the third law (c) third and first laws from the second law (d) All the three laws are independent of each other
Ans: (c) We can derive Newton’s third and first laws from the second law
Newton’s second law measures the (a) acceleration (b) force (c) momentum (d) angular momentum
Ans: (b) Newton’s second law measures the force (Force = mass x acceleration)
A reference frame attached to earth cannot be an inertial frame because (a) earth is revolving around the sun (b) earth is rotating about its axis (c) Newton’s laws are applicable in this frame (d) both (a) and (b)
Ans: (d) An inertial frame of reference is one in which law of inertia holds good i.e. Newton’s laws of motion are applicable equally. If earth is revolving around the sun or earth is rotating about its axis, then forces are acting on the earth and hence there will be acceleration of earth due to these forces. That is why earth can not be an inertial frame of reference.
China wares are wrapped in straw of paper before packing. This is the application of concept of (a) impulse (b) momentum (c) acceleration (d) force
Ans: (a) As a certain impulse applied for a short time will give a large force so the chinaware breaks into pieces. Therefore, chinaware is wrapped in straw of paper while packing so that the event of fall (impact) will take a longer time to reach the chinaware through straw of paper and hence the average force exerted on the chinaware is small and chances of its breaking reduce.
The force of action and reaction (a) must be of same nature (b) must be of different nature (c) may be of different nature (d) may not have equal magnitude
Ans: (a) The force of action and reaction must be of same nature
A body whose momentum is constant must have constant (a) velocity (b) force (c) acceleration (d) All of the above
Ans: (b) It works on the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
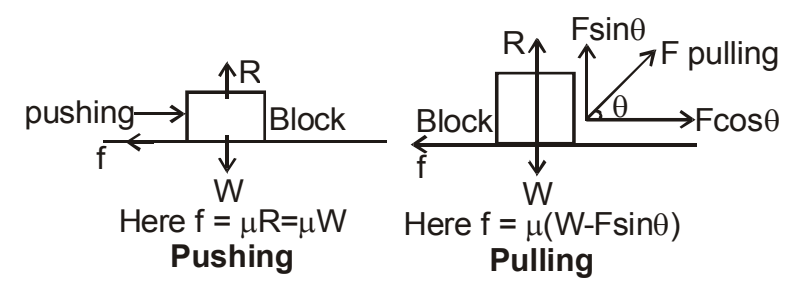
Pulling a roller is easier than pushing because (a) when we pull a roller, the vertical component of the pulling force acts in the direction of weight (b) the vertical component of the pulling force acts in the opposite direction of weight (c) force of friction is in opposite direction (d) it is possible in the case of roller only
Ans: (b) Pulling a roller is easier than pushing because the vertical component of the pulling force acts in the opposite direction of weight
A bullet of mass 10 gm is fired from a gun of mass 1 kg. If the recoil velocity is 5 ms–1, the velocity of muzzle is (a) 0.05 ms–1 (b) 5 ms–1 (c) 50 ms–1 (d) 500 ms–1
Ans: (d) A bullet of mass 10 gm is fired from a gun of mass 1 kg. If the recoil velocity is 5 ms–1, the velocity of muzzle is 500 ms–1
The direction of impulse is (a) same as that of the net force (b) opposite to that of the net force (c) same as that of the final velocity (d) same as that of the initial velocity
Ans: (a) The direction of impulse is same as that of the net force
A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 20 kg for 10 seconds. Change in its momentum is (a) 5 kg m/s (b) 100 kg m/s (c) 200 kg m/s (d) 1000 kg m/s
Ans: (b) A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 20 kg for 10 seconds.
Change in momentum = F × t = 10 × 10 = 100 Ns or 100 kg. m/s
A machine gun of mass M fires n bullets per second. The mass and speed of each bullet is m and v respectively. The force exerted on the machine gun is (a) zero (b) mvn (c) Mvn (d) Mvn/m
Ans: (b) From Newton’s second law, the total external applied force on the body is equal to the time rate change of momentum of the body.
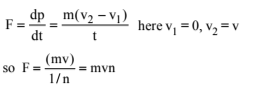
A long jumper runs before jumping because he (a) covers a greater distance (b) maintains momentum conservation (c) gains energy by running (d) gains momentum
Ans: (b) A long jumper runs before jumping to maintain momentum. This helps in jumping higher and longer because of inertia of motion gained due to the motion.
The resultant of force of 5N and 10N cannot be (a) 12 N (b) 8 N (c) 4 N (d) 5 N
Ans: (c) F max =5+10=15N and
F min =10−5=5N ;
Range of resultant 5≤F≤15 ;
therefore , 4N can't be the resultant of these two force
The momentum is most closely related to (a) force (b) impulse (c) power (d) kinetic energy
Ans: (b) The momentum is most closely related to impulse
Which of the following groups of forces could be in equilibrium (a) 3N, 4N, 5 N (b) 4N, 5N, 10 N (c) 30 N, 40 N 80N (d) 1 N, 3 N, 5 N
Ans: (a) For the equilibrium of force, the resultant of two smaller is equal and opposite to third one.
C2=A2+B2
Which of the following statements about friction is true? (a) Friction can be reduced to zero (b) Frictional force cannot accelerate a body (c) Frictional force is proportional to the area of contact between the two surfaces (d) Kinetic friction is always greater than rolling friction
Ans: (d) u static > u kinetic >u rolling
Which of the following is a self adjusting force? (a) Static friction (b) Limiting friction (c) Dynamic friction (d) Sliding friction
Ans: (a) Static friction is a self adjusting force in magnitude and direction.
If u(s), u(k) and u(r) are coefficients of static friction, sliding friction and rolling friction, then (a) u(s) < u(k) < u(r) (b) u(k) < u(r) < u(s) (c) u(r) < u(k) < u(s) (d) u(r) = u(k) = u(s)
Ans: (c) u(r) < u(k) < u(s)
Which of the following statements is correct, when a person walks on a rough surface? (a) The frictional force exerted by the surface keeps him moving (b) The force which the man exerts on the floor keeps him moving (c) The reaction of the force which the man exerts on floor keeps him moving (d) None of these
Ans: (c) When the men push the rough surface on walking, then surface (from Newton’ third Law) applies reaction force in forward direction. It occurs because there is friction between men & surface. If surface is frictionless (such as ice), then it is very difficult to move on it.
It is difficult to move a cycle with brakes on because (a) rolling friction opposes motion on road (b) sliding friction opposes motion on road (c) rolling friction is more than sliding friction (d) sliding friction is more than rolling friction
Ans: (d) When brakes are on, the wheels of the cycle will slide on the road instead of rolling there. It means the sliding friction will come into play instead of rolling friction. The value of sliding friction is more than that of rolling friction.
A rectangular block is placed on a rough horizontal surface in two different ways as shown, then F F (a) (b) (a) friction will be more in case (a) (b) friction will be more in case (b) (c) friction will be equal in both the cases (d) friction depends on the relations among its dimensions.
Ans: (c) A rectangular block is placed on a rough horizontal surface in two different ways as shown, then friction will be equal in both the cases
A car moving on a horizontal road may be thrown out of the road in taking a turn (a) by the gravitational force (b) due to the lack of proper centripetal force (c) due to the rolling frictional force between the tyre and road (d) due to the reaction of the ground
Ans: (b) A car moving on a horizontal road may be thrown out of the road in taking a turn due to the lack of proper centripetal force
By applying a force of one Newton, one can hold a body of mass (a) 102 grams (b) 102 kg (c) 102 mg (d) None of these
Ans: (a) By applying a force of one Newton, one can hold a body of mass 102 grams
The effect of frictional force may be minimized by (a) using a smooth object (b) using a smooth plane (c) providing a lubricant at the surface of contact (d) All of these
Ans: (d) The effect of frictional force may be minimized by using a smooth object, using a smooth plane or by providing a lubricant at the surface of contact.
If an object is in a state of equilibrium (a) it is at rest (b) it is in motion at constant velocity (c) it is in free fall (d) may be more than one of the above
Ans: (d)
If a boat is moving along at constant speed, it may be assumed that (a) a net force is pushing it forward (b) the sum of only vertical forces is zero (c) the buoyant force is greater than gravity (d) the sum of all forces is zero
Ans: (d) If a boat is moving along at constant speed, it may be assumed that the sum of all forces is zero
If A and B are two objects with masses 6 kg and 34 kg respectively, then (a) A has more inertia than B (b) B has more inertia than A (c) A and B have same inertia (d) None of the two has inertia
Ans: (b) If A and B are two objects with masses 6 kg and 34 kg respectively, then B has more inertia than A
Click to rate this post!
[Total: 1 Average: 5]