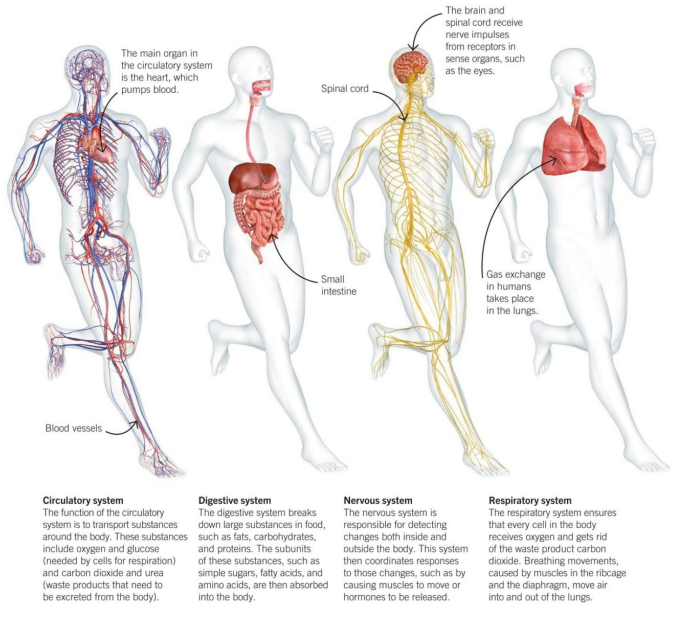
The human body is a biological machine made of body systems; groups of organs that work together to produce and sustain life. Sometimes we get lost while studying cells and molecules and can’t see the forest for the trees. It can be helpful to step back and look at the bigger anatomical picture.
This topic page will provide you with a quick introduction to the systems of the human body so that every organ you learn later on will add a superstructure to the basic concept you adopt here.

Key facts about the human body systems
| System of organs | A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions in the body. |
| Musculoskeletal system | Mechanical support, posture and locomotion |
| Cardiovascular system | Transportation of oxygen, nutrients and hormones throughout the body and elimination of cellular metabolic waste |
| Respiratory system | Exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide between the body and air, acid-base balance regulation, phonation. |
| Nervous system | Initiation and regulation of vital body functions, sensation and body movements. |
| Digestive system | Mechanical and chemical degradation of food with purpose of absorbing into the body and using as energy. |
| Urinary system | Filtration of blood and eliminating unnecessary compounds and waste by producing and excreting urine. |
| Endocrine system | Production of hormones in order to regulate a wide variety of bodily functions (e.g. menstrual cycle, sugar levels, etc) |
| Lymphatic system | Draining of excess tissue fluid, immune defense of the body. |
| Reproductive system | Production of reproductive cells and contribution towards the reproduction process. |
| Integumentary system | Physical protection of the body surface, sensory reception, vitamin synthesis. |
Skeletal system
The skeletal system is composed of bones and cartilage. There are two parts of the skeleton; axial and appendicular. The axial skeleton consists of the bones of the head and trunk. The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones within the limbs, as well as supporting pectoral and pelvic girdles.
There are 206 bones in an adult human body. The place at which two bones are fitted together is called the joint or articulation. Joints are supported by cartilages and reinforced with ligaments. The functions of the skeletal system are mechanical support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium storage, and endocrine regulation.
Elements of the skeletal system are adjusted to the function of the body part they support. Thus, the anatomy of bones, joints, and ligaments is studied topographically, as the bones of the; head and neck, thorax, abdomen, and upper and lower limbs.